In laser diodes beam divergence is specified with two values because of the presence of astigmatism see diodes vs.
Laser beam divergence measurement.
This definition yields a divergence half angle.
Beam divergence is defined in the far field where the beam divergence is constant.
For laser beams for which the second order moments of intensity beam width and divergence can be determined the beam propagation ratio m 2 is often used to characterize beam quality.
Dataray offers a full range of iso 11146 compliant beam profilers both camera and scanning slit based which provide multiple methods of measuring beam divergence.
Beam divergence is defined by the full angle.
The beam divergence defines how much the beam spreads out over increasing distance from the optical aperture.
You know that bell shaped curve telling you that most of the beam energy is located at the center of the beam along the propagation axis.
By design circular laser beams usually possess a gaussian shaped energy density distribution or irradiance from the center of the beam to the edges.
The term is relevant only in the far field away from any focus of the beam practically speaking however the far field can commence physically close to the radiating aperture.
In electromagnetics especially in optics beam divergence is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter or radius with distance from the optical aperture or antenna aperture from which the beam emerges.
Standard for the measurement of beam widths beam divergence and propagation factors proposal for a working draft iso tc 172 sc 9 wg 1 april 29 1992.
The divergence of a laser beam can be calculated if the beam diameter d 1 and d 2 at two separate distances are known.
It is usually defined as the derivative of the beam radius with respect to the axial position in the far field i e in a distance from the beam waist which is much larger than the rayleigh length.
The m 2 factor compares the actual shape of the beam to that of an ideal gaussian beam.
A low beam divergence can be important for applications such as pointing or free space optical communications.
The beam divergence of a laser beam is a measure for how fast the beam expands far from the beam waist i e in the so called far field.
Laser beam divergence measurement is all about beam size.
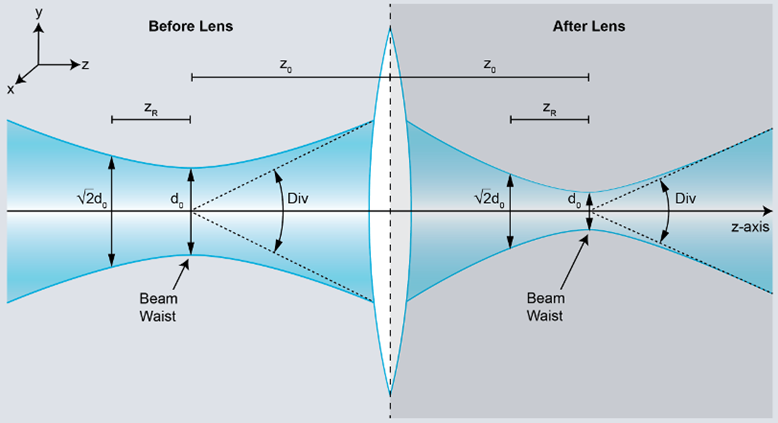
The focal length divergence method provides a means for finding the far field beam divergence at any point in the beam propagation path.
The focal length divergence measurement method the focal length divergence measurement method is based upon the beam width of a focused beam s spot size and the focal length of the focusing optic.
In this case the orientation of the beam divergence needs to be.
The beam divergence of a laser beam is a measure for how fast the beam expands far from the beam waist.